Displaying changes on different operating systems
There are a lot of git clients out there, but the one and only truth shows your CLI. A simple workflow to achieve this is:
-
git fetch origin -pfetches the most current data from youroriginrepository and cleans up any no longer existing references. -
git statusshows the status of the working directory, about tracked files and their staged state. -
git logshows the history of the working directory. HitSPACEshow more content andqto quite the view.
bakka$ git log
commit 45e9143531ef8d9a67845fcf62904b93ece34658
Author: Kacper Bak <github@kacperbak.de>
Date: Sun Oct 4 19:34:08 2015 +0200
Added more text
commit 174b974b227f09a06ee3323aecc3fdbc803c7a2b
Author: Kacper Bak <github@kacperbak.de>
Date: Sun Oct 4 18:25:42 2015 +0200
Started git changes content...
commit d49d54935226ce8bf1c6130a9e2d11d040b07b91
Author: Kacper Bak <github@kacperbak.de>
Date: Sun Sep 13 18:36:24 2015 +0200
Setting up a Git on the CLI - content added
...
This is very verbose, to reduce the noise type: git log --oneline
bakka$ git log --oneline 45e9143 Added more text 174b974 Started git changes content... d49d549 Setting up a Git on the CLI - content added 886b9be Basic Bash content added
To see a tree view like in many typical GUI tools for git use: git log --graph --decorate --oneline
bakka$ git log --graph --decorate --oneline * 45e9143 (HEAD, origin/feature/git-display-branches, feature/git-display-branches) Added more text * 174b974 Started git changes content... * d49d549 (origin/master, origin/HEAD, master) Setting up a Git on the CLI - content added * 886b9be Basic Bash content added * 411434b Basic Bash content added * abb9055 Basic Bash content added * 40a24fa Mac-os-x-tools article deleted * 95a69b6 Generated all files with adoc 1.5.2 * f289e9a Merge branch 'Daily-git-usage' |\ | * 965dc97 Git section added | * 963d9e3 Daily git usage added |/ * 7c50a9b Test new content
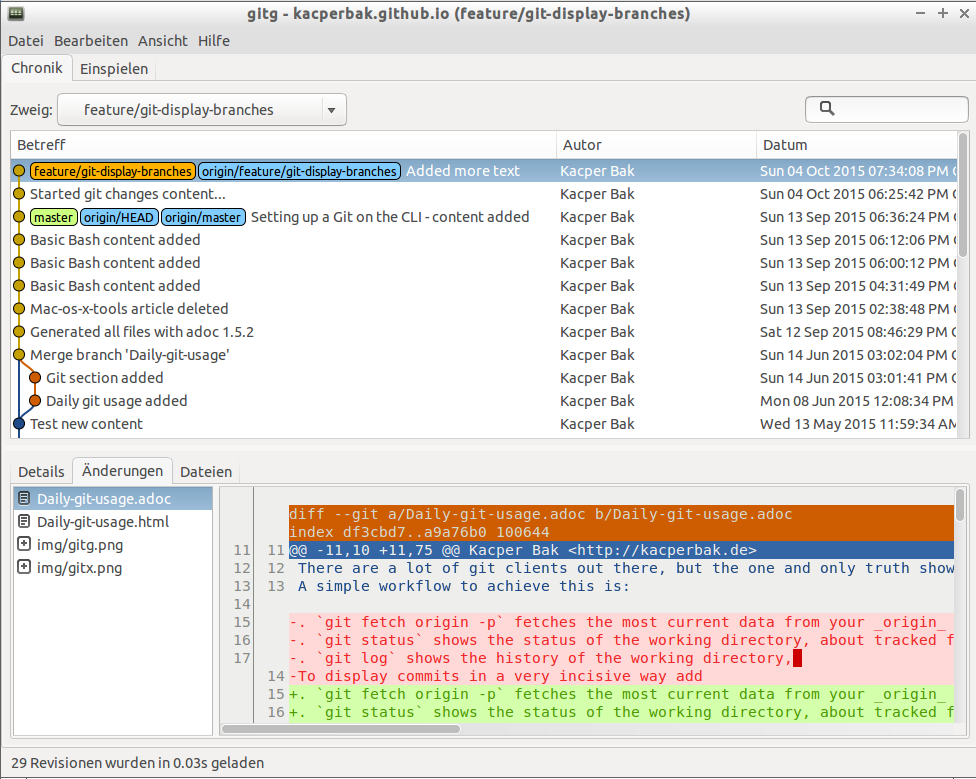
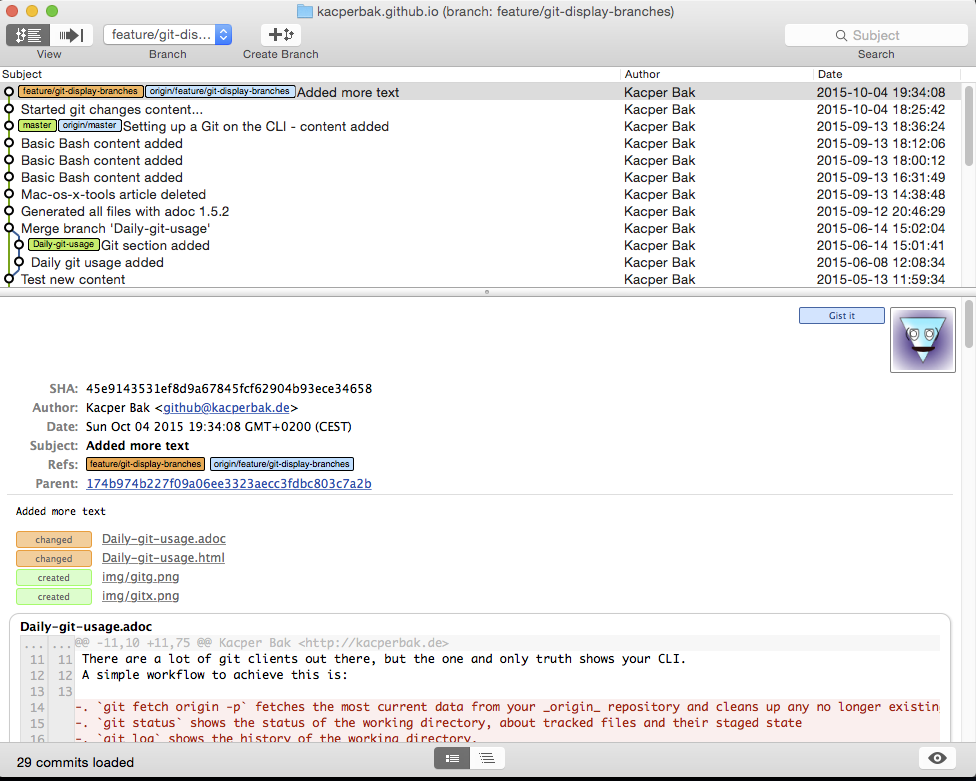
It is always nice to have a more sophisticated UI, just be aware that those tools might not always show the current state of your working directory. Two light weight ones are gitg (for Ubuntu) or gitx (for Mac OS X) both can be simple started directly from your working directory by hitting its name.
$ gitg
$ gitx
Setting up a Git on the CLI
There are a few convenience settings to use Git very smoothly from your command line interface like bash. Simple follow the links to achieve the wanted result:
Setting your user name and email in Git
git config --global user.name "Kacper Bak" git config --global user.email "github@kacperbak.de"
Checking your username and email in Git
git config --global user.name git config --global user.email
Enable CLI auto completion with tabulator key (Mac OS X)
-
Download the file
git-completion.bashfrom the git-repository. -
Copy it into your home folder like
/Users/kaba/git-completion.bash -
Enter the following into your
.bash_profile
source ~/git-completion.bash
Setup basic aliases
git config --global alias.co checkout git config --global alias.br branch git config --global alias.ci commit git config --global alias.st status git config --global alias.lg "log --color --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset' --abbrev-commit"
Shows the current branch in the bash prompt
-
Download the file
git-prompt.shfrom the git-repository. -
Copy it into your home folder like
/Users/kaba/git-prompt.sh -
Enter the following into your
.bash_profile
source ~/git-prompt.sh PS1="[\[\033[32m\]\w]\[\033[0m\]\$(__git_ps1)\n\[\033[1;36m\]\u\[\033[32m\]$ \[\033[0m\]"
Number of commits per user
git shortlog -sne
Working with a local test repository
-
We assume that we are in an empty folder
-
Create a local repository with the name
testrepo.
git init --bare testrepo
-
Type
ls -alto get an overview. -
As you can see the last command created a directory with the name
testrepo. -
To clone that repo we need the exact file system path. So type
pwdto get your current location. -
Now you can
clonethe repo with the following command.
git clone file:///Users/bakka/Projects/gitRepos/testrepo
-
As you can see, the
testreponame has been added to the end of the absolut path. -
The command is using the
fileprotocoll as we operate on our local machine.
Checkout a file from another branch
git checkout otherbranch myfile.txt
Revert to HEAD and reset ALL changes made
git reset --hard HEAD git clean -fd